You have a computer literacy course in your university. In the computer
system, the login/logout records of all PCs in a day are stored in a
file. Although students may use two or more PCs at a time, no one can
log in to a PC which has been logged in by someone who has not
logged out of that PC yet.
You are asked to write a program that calculates the total time of a
student that he/she used at least one PC in a given time period
(probably in a laboratory class) based on the records in the file.
The following are example login/logout records.
- The student 1 logged in to the PC 1 at 12:55
- The student 2 logged in to the PC 4 at 13:00
- The student 1 logged in to the PC 2 at 13:10
- The student 1 logged out of the PC 2 at 13:20
- The student 1 logged in to the PC 3 at 13:30
- The student 1 logged out of the PC 1 at 13:40
- The student 1 logged out of the PC 3 at 13:45
- The student 1 logged in to the PC 1 at 14:20
- The student 2 logged out of the PC 4 at 14:30
- The student 1 logged out of the PC 1 at 14:40
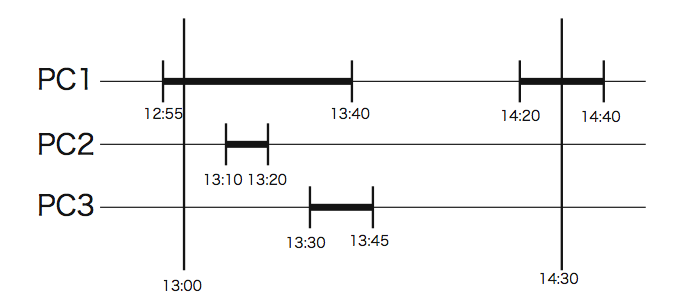
For a query such as "Give usage of the student 1 between 13:00 and
14:30", your program should answer "55 minutes", that is, the sum of
45 minutes from 13:00 to 13:45 and 10 minutes from 14:20 to 14:30, as
depicted in the following figure.
The input is a sequence of a number of datasets.
The end of the input is indicated by a line containing two zeros
separated by a space.
The number of datasets never exceeds 10.
Each dataset is formatted as follows.
N M
r
record1
...
recordr
q
query1
...
queryq
The numbers N and M in the first line are the numbers of
PCs and the students, respectively. r is the number of
records. q is the number of queries. These four are integers
satisfying the following.
1 ≤ N ≤ 1000, 1 ≤ M ≤ 10000, 2 ≤ r ≤ 1000, 1 ≤ q ≤ 50
Each record consists of four integers, delimited by a space, as follows.
t n m s
s is 0 or 1.
If s is 1, this line means that the student m logged in
to the PC n at time t . If s is 0, it means that
the student m logged out of the PC n at time t .
The time is expressed as elapsed minutes from 0:00 of the day.
t , n and m satisfy the following.
540 ≤ t ≤ 1260,
1 ≤ n ≤ N , 1 ≤ m ≤ M
You may assume the following about the records.
Records are stored in ascending order of time t.
No two records for the same PC has the same time t.
No PCs are being logged in before the time of the first record
nor after that of the last record in the file.
Login and logout records for one PC appear alternatingly, and each of the login-logout record pairs is for the same student.
Each query consists of three integers delimited by a space, as follows.
ts te m
It represents "Usage of the student m between
ts and te ".
ts , te and m
satisfy the following.
540 ≤ ts < te ≤ 1260,
1 ≤ m ≤ M
4 2
10
775 1 1 1
780 4 2 1
790 2 1 1
800 2 1 0
810 3 1 1
820 1 1 0
825 3 1 0
860 1 1 1
870 4 2 0
880 1 1 0
1
780 870 1
13 15
12
540 12 13 1
600 12 13 0
650 13 15 1
660 12 15 1
665 11 13 1
670 13 15 0
675 11 13 0
680 12 15 0
1000 11 14 1
1060 12 14 1
1060 11 14 0
1080 12 14 0
3
540 700 13
600 1000 15
1000 1200 11
1 1
2
600 1 1 1
700 1 1 0
5
540 600 1
550 650 1
610 620 1
650 750 1
700 800 1
0 0
