Links
Problem A
Count Down Up 2020
The countdown to the Olympic and Paralympic Games Tokyo 2020 continues until summer 2021. That aside, you are asked to count up the occurrences of the four integers 2, 0, 2, and 0 appearing consecutively in this order in given lists of integers.
Input
The input consists of multiple datasets, each in the following format.
n
d1 … dn
Each of the datasets consists of two lines. The first line has an integer n (4 ≤ n ≤ 1000), which is the number of integers listed in the second line. The second line contains n integers d1, …, dn separated by spaces. Here, all of d1 to dn are between 0 and 9, inclusive.
The end of the input is indicated by a line containing a zero.
The number of datasets does not exceed 100.
Output
For each of the datasets, output one line containing the number of times the four integers 2, 0, 2, and 0 appear consecutively in this order in the list of integers in its second line. Overlapping occurrences are separately counted. “2 0 2 0 2 0 2 0”, for example, is said to have three occurrences, rather than two.
Sample Input
15 2 0 2 0 2 2 0 2 0 2 2 0 2 0 2 20 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 32 1 8 1 9 1 9 2 0 2 0 2 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 1 2 0 2 0 1 9 1 9 1 8 32 2 0 1 8 2 0 1 9 2 0 2 0 2 0 2 1 2 0 2 2 2 0 2 3 2 0 2 1 2 0 2 0 0
Output for the Sample Input
3 0 2 3
Problem B
Contact Tracer
Novel virus infections are spreading. The virus is known to transmit on close contact with carriers, whether or not with any symptoms. Therefore, it is effective for epidemic prevention to identify and test those who had close contact with persons confirmed or were judged highly probable to be infected. To realize this, a system is desired that perpetually records all the close contact events by an application on mobile phones and, when infection is confirmed, identifies all persons with direct or indirect infection risks based on the record.
You were asked to develop such a system, and have already finished the mobile phone part. When the installed application detects a close contact event with another person carrying a phone with the same application installed, it sends IDs of both to the surveillance center.
Your next task is to develop a program that, when infection of a user is confirmed, identifies users with risks of direct or indirect transmission from the infected user.
When a user of the system is confirmed to be infected, those users who made close contacts with the infected user within a certain time period (period of communicability) are suspected of infection. If a suspected user had close contact with still another user after that possible infection event, that user also is suspected of infection. The suspects are propagated repetitively in this manner.
When a user is confirmed infected, the ID of the user and the list of all the close contact events of all users with all users happened after the time when the confirmed user possibly becomes a carrier are given. All the events in the given list should be assumed to be within the period of communicability of the confirmed user. The output should be the number of users to whom the virus was possibly transmitted directly or indirectly from the infected user.
Input
The input consists of multiple datasets, each in the following format.
m n p
a1 b1
…
an bn
Each of the datasets starts with a line containing three integers: m (1 ≤ m ≤ 100) is the number of users, n (0 ≤ n ≤ 1000) is the number of events in the list, and p (1 ≤ p ≤ m) is the ID of the user confirmed to be infected.
The following n lines contain the close contact events between users, one event per line, in time order. Each line indicates that the users whose IDs are ai and bi had close contact. Here, ai and bi satisfy 1 ≤ ai ≤ m, 1 ≤ bi ≤ m, and ai ≠ bi.
The end of the input is indicated by a line containing three zeros. The number of datasets does not exceed 50.
Output
For each dataset, output a single line containing the total number of users including the user confirmed to be infected and users to whom the virus was possibly transmitted directly or indirectly from the confirmed user.
Sample Input
3 2 1 1 2 2 3 4 5 2 1 3 3 4 2 1 3 1 1 2 100 0 100 0 0 0
Output for the Sample Input
3 3 1
Problem C
Luggage
Mr. Yokohama is estimating the delivery fare for a number of luggage pieces. The fare for a piece is determined by its width w, depth d and height h, each rounded up to an integer. The fare is proportional to the sum of them.

The list of the luggage pieces is at hand, but the list has the product w×d×h for each piece, instead of the sum w+d+h by mistake. This information is not enough to calculate the exact delivery fare.
Mr. Yokohama therefore decided to estimate the minimum possible delivery fare. To this end, given the listed product p for each of the luggage pieces, the minimum possible sum s=w+d+h satisfying p=w×d×h should be found.
You are requested to help Mr. Yokohama by writing a program that, when given the product p, computes the minimum sum s.
Input
The input consists of multiple datasets. Each of the datasets has one line containing an integer p (0 < p < 1015).
The end of the input is indicated by a line containing a zero.
The number of datasets does not exceed 300.
Output
For each dataset, output a single line containing an integer s. s should be the minimum possible sum w+d+h of three positive integers, w, d, and h, satisfying p=w×d×h.
Sample Input
1 2 6 8 729 47045881 12137858827249 562949953421312 986387345919360 999730024299271 999998765536093 0
Output for the Sample Input
3 4 6 6 27 1083 6967887 262144 298633 299973 999998765536095
Problem D
Icpcan Alphabet
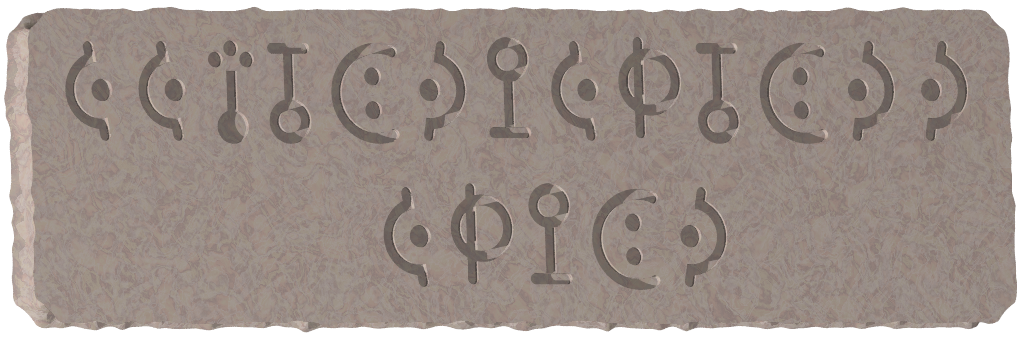
Research on the civilization of old kingdom of Icpca has been carried out at the Investigation Center for Prehistoric Civilization (ICPC). Their recent excavation found two expressions engraved on a stone wall at the ruins of Icpca. The expressions are composed of n distinct Icpca letters a1, ..., an, symbols corresponding to inequality signs ('<' and '>') and parentheses ('(' and ')'). In what follows, they are represented by capital Roman letters and ordinary symbols for description ease. Expressions conform to the following grammar rules with the start symbol E.
E ::= F | '(' E '<' E ')' | '(' E '>' E ')'
F ::= a1 | a2 | … | an
Analyses unifying multifarious knowledge on the old kingdom and its civilization revealed the following evaluation rules.
- A total order relation is defined on the set of letters a1, ..., an.
- When an expression consists only of a single letter, the value of the expression is that very letter.
- For two expressions P and Q with values ai and aj, respectively, the value of the expression (P<Q) is one of the letters ai or aj that precedes in the total order. If the two letters are the same, the value is that letter.
- Similarly, for two expressions P and Q with values ai and aj, respectively, the value of the expression (P>Q) is one of the letters ai or aj that comes later in the total order. If the two letters are the same, the value is that letter.
It was also found that the values of the two expressions discovered must be equal. How many different total orders, among n! possible total orders, make the values of the two expressions equal?
Input
The input consists of multiple datasets, each in the following format.
n
a1a2...an
S
T
Each dataset consists of four lines. The first line contains n (1 ≤ n ≤ 16), the number of different capital Roman letters corresponding to Icpcan characters. The second line contains n distinct capital Roman letters without any spaces. The third and the fourth lines contain two discovered expressions S and T, respectively. Both S and T conform to the grammar given above and neither of them has more than 100 characters.
The end of the input is indicated by a line containing a zero. The number of datasets does not exceed 50.
Output
For each dataset, output a single line containing the number of different total orders making the values of the two expressions equal.
Sample Input
3 CIP ((I<C)>(P<C)) (P>C) 2 AB (A<B) (A>B) 3 ANY ((A<N)<Y) ((N<Y)<((A<A)<N)) 6 ANSWER A ((E>(A>((E<W)>(N<S))))>(A<W)) 0
Output for the Sample Input
1 0 6 300
Problem E
Keima
You are given a set of points aligned in a grid of N rows and M columns. Each of the points is named Pi, j with its row number i (1 ≤ i ≤ N) and its column number j (1 ≤ j ≤ M).
Each point is colored either white or black. Your task is to compute the number of subsets T of white points satisfying the following conditions:
- ∀i ∈ {3, 4,..., N}, ∀j ∈ {2, 3,..., M}, Pi, j ∈ T ⇒ Pi -2, j -1 ∉ T,
- ∀i ∈ {3, 4,..., N}, ∀j ∈ {1, 2,..., M−1}, Pi, j ∈ T ⇒ Pi -2, j +1 ∉ T.
For example, in the figure below, if you include the point marked with a star to the set T, you can include neither of the two crossed points.
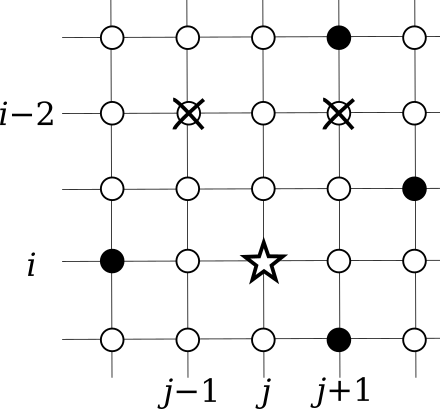
If you are familiar with the game of shogi (Japanese chess), you may find similarities between the possible moves of a keima with the relative positions of the star point and crossed points.
Because the answer can be huge, output the remainder divided by 109+7.
Input
The input consists of multiple datasets, each in the following format.
N M
a1,1 ... a1,M
...
aN,1 ... aN,M
The first line of each dataset contains two integers N (2 ≤ N ≤ 60) and M (2 ≤ M ≤ 60) representing the numbers of rows and columns of the grid, respectively. Each of the following N lines contains M characters. The j-th character of the i-th line, ai,j, represents the color of the point Pi, j, where '.' denotes white and '#' denotes black.
The end of the input is indicated by a line containing two zeros.
The number of datasets does not exceed 100.
Output
For each dataset, output one line containing the number of subsets satisfying the conditions modulo 109+7.
Sample Input
3 2 .# ## #. 3 3 .#. #.# ..# 6 5 .#..# ...#. #.... ..#.# #.... ..#.. 0 0
Output for the Sample Input
3 20 103320
Problem F
Evacuation Site
The council of your home city decided to build a public evacuation site to prepare for natural disasters. The evacuation site is desired to be built at a location reachable from as many locations across the city as possible, even when many road segments are closed due to a natural disaster. Given the road network of the city, please find the best candidate locations.
The road network is specified as an undirected graph. The nodes of the graph correspond to various locations in the city area, and the edges are two-way road segments connecting the locations. Each road segment is assigned a positive integer representing the assumed strength against disasters. A road segment with assumed strength s is expected to be available on a disaster of level below s, but will be closed on a disaster of level above or equal to s.
Adequacy of a location as an evacuation site is assessed by the following ordering. Let us define rs(v) as the number of locations that is directly or indirectly connected to the location v via road segments available even on the level-s disaster. We define the location u is more suitable than the location v as an evacuation site if and only if there exists some k ≥ 1 satisfying
- r1(u) = r1(v),
- r2(u) = r2(v),
- ...
- rk-1(u) = rk-1(v), and
- rk(u) > rk(v).
Input
The input consists of multiple datasets, each in the following format.
n m
a1 b1 s1
...
am bm sm
n is a positive integer less than or equal to 105, representing the number of locations. m is a non-negative integer less than or equal to 105, representing the number of road segments. The locations in the city are given ID numbers 1 through n. The i-th segment connects the locations ai and bi, and its assumed strength is si. Each of ai, bi, and si is an integer and they satisfy 1 ≤ ai < bi ≤ n and 1 ≤ si ≤ 105. When i ≠ j, either ai ≠ aj or bi ≠ bj holds. The given graph is connected. That is, there is at least one path between every pair of locations.
The end of the input is indicated by a line containing two zeros. The number of datasets does not exceed 50.
Output
For each dataset, output the list of the ID numbers of all of the locations most suitable with the criterion described above separated by a space character, in the increasing order, in a line.
Sample Input
3 3 1 2 1 1 3 2 2 3 3 3 3 1 2 3 1 3 3 2 3 3 5 5 1 2 5 2 3 1 3 4 2 3 5 1 4 5 2 0 0
Output for the Sample Input
2 3 1 2 3 3 4 5
Problem G
Avoiding Three Cs
You are a member of ICPC Company, and planning to place seats in the new office. Your task is to place as many seats as possible in the room while satisfying the conditions for avoiding three Cs. You decided to solve the problem through simulation on a grid.
In the simulation, the room is expressed by a rectangular grid. Each cell in the grid is either empty where you can place a seat, or a wall cell where you cannot place a seat. You cannot place two or more seats in the same empty cell to keep the distance between seats.
Hereinafter, a route starting from the cell at the northwest corner, repeating moves to the east or to the south, finally reaching the cell at the southeast corner, is called a ventilation route. There may exist many ventilation routes. For any cell with a seat placed, it must be on at least one ventilation route. Moreover, the number of seats on any ventilation route, called the seat passing number, must not exceed the given maximum. Your task is to find seat placements in the room that have as many seats as possible.
Input
The input consists of multiple datasets. Each dataset is represented in the following format.
n m k
a1,1…a1,m
…
an,1…an,m
n and m are the height and width of the given grid. n and m are positive integers not exceeding 20. k is the maximum allowed seat passing number. k is a positive integer not exceeding n + m − 1. Each of the following n lines contains m characters, either '.' or '#', denoting the cells of the grid. If ai,j equals '.', the corresponding cell is empty. If it equals '#', the cell is a wall. The cell at row 1 and column 1 is at the northwest corner of the room, and the cell at row n and column m is at the southeast corner.
The end of the input is indicated by a line containing three zeros. The number of datasets does not exceed 100.
Output
For each of the datasets, output the following n + 1 lines. The first line should contain the maximum possible number of seats that can be placed. The second and subsequent lines should contain one of the placements with the maximum number of seats. The output of the placements should be in the same format as given in the input, except that cells with a seat placed should be represented as '@' instead of '.'. If there are two or more placements with the maximum possible number of seats, output one with the first in the dictionary order in the ASCII codes when all the lines of their representations are concatenated. Note that '#' < '.' < '@' holds in ASCII codes.
Sample Input
3 3 3 ... .#. ... 3 3 1 ... .#. ... 6 11 1 ........... .....#..... .....#..... .....#..... .....#..... ........... 7 7 3 ....... .##.##. .#...#. .#...#. .#...#. .##.##. ....... 0 0 0
Output for the Sample Input
6 .@@ @#@ @@. 2 ... .#@ .@. 10 ..........@ ....@#...@. ...@.#..@.. ..@..#.@... .@...#@.... @.......... 9 ....... .##.##. .#...#. .#.@.#@ .#.@.#@ .##@##@ @@@....
Problem H
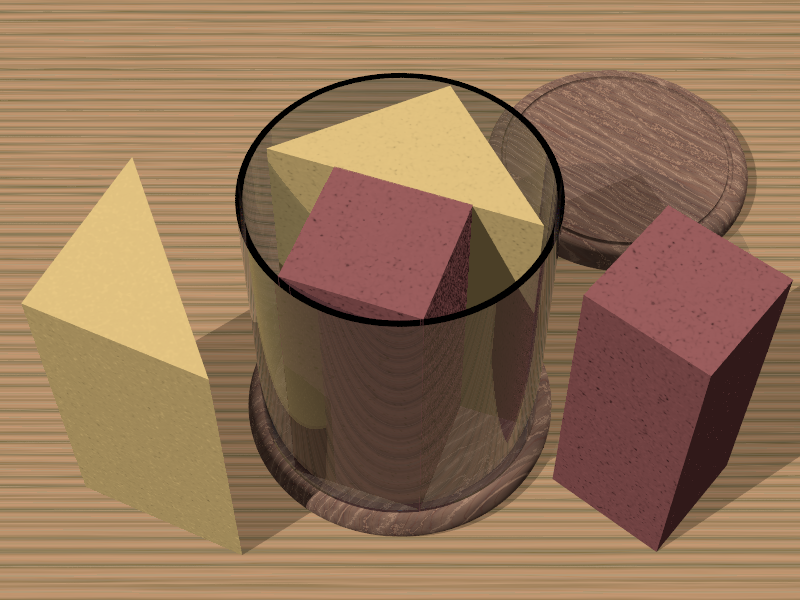
Idealistic Canister
The Ideally Compact Packaging Canisters (ICPC) corporation is a package manufacturer specialized in canisters (cylindrical containers), designing and manufacturing canisters satisfying clients' demands.
The corporation has taken an order of a canister to pack two different products together. Both products have shapes of convex polygonal prisms with the same height. The inside of the canister should be precisely a cylinder whose height is equal to the height of the products.
Products must be placed vertically in the canister, that is, the bottoms of the products must meet the inner bottom of the canister. Products can be placed at an arbitrary position and with an arbitrary direction in the canister, but they should not be laid upside-down nor stacked one on the other. Products and the inner surface of the canister may touch one another.
The customer requests to make the canister as small as possible. Your task is to find the smallest possible diameter of the canister bottom that can contain the two products.
Input
The input consists of at most 50 datasets, each in the following format.
n
xa,1 ya,1
...
xa,n ya,n
m
xb,1 yb,1
...
xb,m yb,m
n (3 ≤ n ≤ 40) is the number of vertices of the bottom polygon of one of the products. The following n lines have two integers each, which are the x- and y-coordinates of the vertices of the bottom polygon. They are between −1000 and 1000, inclusive. The vertices are listed in a counter-clockwise order. The bottom polygon is guaranteed to be convex.
Then comes the description of the bottom polygon of the other product in exactly the same manner.
The end of the input is indicated by a line containing a zero.
Output
For each dataset, output the smallest possible diameter of the bottom circle of the canister that accommodates the two products together. The output must not contain an error greater than 10−6.
Sample Input
3 8 0 7 7 0 6 4 0 0 5 0 5 5 0 5 3 0 0 2 2 0 2 3 3 1 5 1 5 3 5 0 0 3 0 3 1 1 3 0 3 5 0 0 3 0 3 1 1 3 0 3 9 0 0 9 4 13 13 9 22 6 24 -6 24 -9 22 -13 13 -9 4 4 1 0 0 5 -1 0 0 -5 0
Output for the Sample Input
10.625000000000 2.828427124746 5.656854249492 26.000000000000
